What is Methenamine?
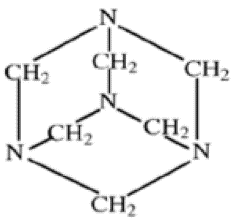
The heterocyclic organic compound hexamine, also referred to as methenamine, has the formula (CH2)6N4. It is extremely soluble in water and polar organic solvents and has a cage-like structure comparable to adamantane. Hexamine has the following characteristics and applications:
Hexamine is used in the manufacture of various organic molecules, such as polymers, drugs, and additives for rubber.
It has anti-infective properties and is frequently used to treat urinary tract infections.
Hexamine is a component of sealing agents, coatings, and adhesives.
Hexamethylenetetramine is a component of hexamine fuel tablets, which are used by campers, hobbyists, the military, and aid organizations to heat camping food or military supplies. These fuel tablets also include 1,3,5-trioxane. Although its gases are hazardous, it burns without producing any smoke, has a high energy density of 30.0 megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg), does not liquefy when burning, and leaves no ashes.
Fire-protection laboratories employ standardized 0.149 g methenamine (hexamine) tablets as a clean and repeatable fire source to test.
Hexamine Characteristics
- Hexamine is a white, crystalline material that smells ammonia-like fish under ambient conditions. At 280 °C, it sublimes in vacuum.
- Although highly combustible and moisture-sensitive, hexamine is stable. Aluminum, zinc, acids, and oxidizing agents are incompatible with it. With certain drugs, it has a strong or explosive reaction.
Hexamine Applications
antibiotic
Hexamine is used as an anti-infective, especially in the treatment of urinary tract infections. It slowly releases formaldehyde, which has antibacterial properties, when hydrolyzed at acidic pH.

Solid fuel tablets
Hexamine is a component of hexamine fuel pellets. These tablets are used by campers, hobbyists, the military, and relief organizations to heat camping food or military rations. Hexamine fuel pellets burn smokeless, have a high energy density and leave no ash.

Adhesives
Hexamine is used in the manufacture of adhesives. It helps to provide strong bonding properties in various applications.
Coatings and sealants
Hexamine is used in the formulation of coatings and sealing compounds. It helps to improve the durability and performance of these products.

Rubber vulcanization
Hexamine acts as a crosslinking agent during the vulcanization of rubber. It helps to improve the durability, elasticity and heat resistance of rubber products.
Synthesis of chemical compounds
Hexamine is used in the synthesis of other chemical compounds, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and rubber additives. It serves as a building block in the production of these materials.
Other applications

synthetic resins

Agriculture
Leather and Textile

Pharmaceuticals
Explosives

Photography
Organic chemicals
Paper Industry
Oil Industry

Metal Industry
alternatives to using hexamine
There are several alternatives to using hexamine in industrial processes. Here are some options:
Other anti-infectives
There are other anti-infectives that can be used to treat urinary tract infections, such as antibiotics such as penicillins and cephalosporins. Renewable energy: Using renewable energy sources can help reduce the environmental impact of hexamine production by reducing consumption of non-renewable energy sources. In summary, there are several alternatives to the use of hexamine in industrial processes. These alternatives can help reduce the environmental impact of hexamine production and use.
TAT, DADN and DANNO
These are alternative procedures for the preparation of HMX, a high-energy explosive, from hexamine. Other cross-linking agents: There are other crosslinking agents that can be used in the vulcanization of rubber, such as sulfur and peroxides.
Phenolic Resin
Phenolic resins can be used as an alternative to hexamine in the manufacture of adhesives, coatings and sealing compounds.


